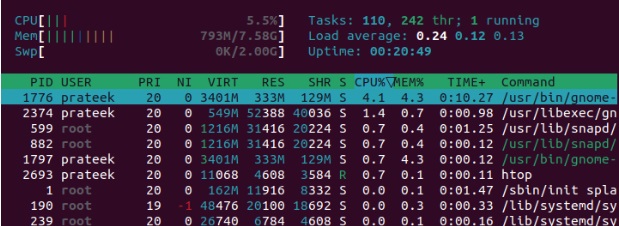
The htop is a CLI energy to inspect an interactive list of running procedures in real-time. It is an extra feature-rich and easy to use choice to the leading command. The htop command allows you to take care of system procedures, monitor resources, and execute various other management tasks.
One of one of the most prominent functions of htop is that it shows color-coded processes, which helps you separate them based on resource usage. Moreover, it lets you personalize the outcomes with its sort and filter options. So, this short tutorial has to do with exactly how to utilize the htop command in Linux without hassles. Unlike top, the htop command is not preinstalled in the majority of Linux systems. That’s why you must install it making use of the following commands:
| Operating System | Command |
| Debian/Ubuntu | sudo apt-get set up htop |
| Fedora | sudo dnf set up htop |
| RHEL/CentOS | sudo yum install htop |
Currently, you can make use of the htop command, so allow’s begin with the basics:
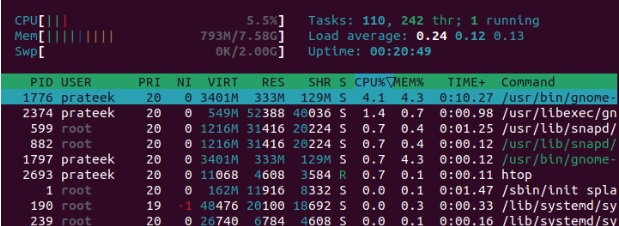
When you execute the above command, it launches the htop energy. Below, you can make use of the arrow keys to navigate up and down the procedures. Additionally, press ‘F 1 or ‘?’ to get the help screen for added navigating faster ways.
Sort Procedures in htop
In htop, you can sort the processes by CPU, memory, and various other use. Open the arranging menu by pushing F 6:
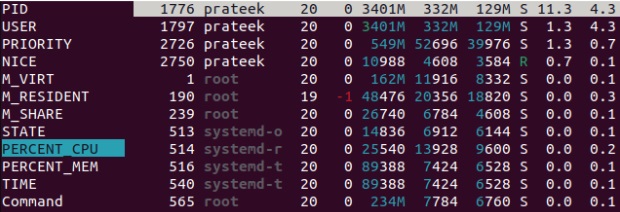

For instance, select the PERCENT_CPU option and press ‘Enter.’
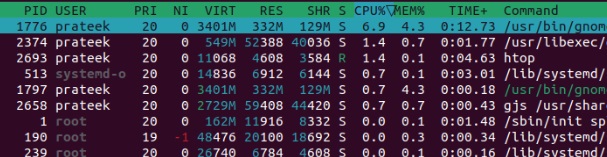

As you can see in the above photo, all the processes are now arranged by CPU usage.
Browse and Filter Processes in htop
To search any process in htop, please undergo the adhering to steps:
Press ‘F 3 to open up the search bar.

In a similar way, press ‘F 4 to filter out the procedures.
Added Choices with htop
-d,– hold-up= [argument]: By default, htop updates the procedures every 2nd, yet you can include a hold-up using this option. As an example, to introduce a delay of 10 secs, we would certainly enter ‘– hold-up= 10’

-C,– no-color: This alternative disables the shade result, which is handy in systems with restricted incurable assistance for shades.

-u,– individual= [username]: To show the processes for a details individual. Simply change’ [username] with the target user’s name.
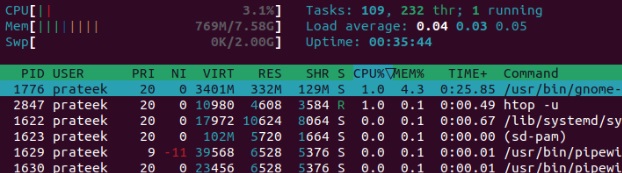

-p,– pid= [PID1,PID2]: Displays information for specified procedure IDs. For instance, allow’s examine the details of PID 1:

-v,– version: Prints htop version information.


-h,– aid: This displays a help message with use information.

Eliminate a Process in htop
If you want to kill any type of procedure, select it and press the ‘F 9 essential or ‘k’ to send a kill signal for the chosen process.
Completing
Htop is a powerful utility for interactively inspecting system procedures in genuine time. This tutorial briefly discusses just how to make use of the htop command. As htop is not a preinstalled utility in Linux circulations, your first step is to install it using the discussed commands. Later on, we described just how to arrange, look, filter, and eliminate processes from the htop energy.