Tails is a Tor-based project influenced by the Debian Linux distro. Tails service Tor Structure, i.e., the onion router. It is meant to be a safe and secure OS and tough to map with average tools/tricks.
Tails is used to do privacy-focused tasks without leaving digital traces. These jobs consist of accessing or checking the target, i.e., it is recommended to access the identification type of information fairly (with permission of the target).
Today, this guide brings a brief walkthrough of the Tails OS and additionally provides the procedure to set up Tails.
Tails OS|A Quick Walkthrough
Allow’s have a quick walkthrough of the functions, some realities, and devices that Tails has:
Tails Development and Merger With Tor
- Tails was initial released in 2009 as an iteration of Incognito, a Gentoo-based Linux distribution.
- The Tails task was originally called” Amnesia, and currently” Amnesia is the default username/hostname of the Tails OS.
- In 2023, the Tails sent a demand to merge with Tor, which was finished in 2024, and now Tails is a Tor task.
Release Cycle
- Tails typically release the update after every 6 – 8 weeks. Nevertheless, the major launch (Like 5.0, 6.0, 7.0) is expected approximately every 2 years.
Top Attributes of Tails OS
- Interaction by means of Tails is done making use of Tor (The Onion Router).
- Straight or non-Tor website traffic is blocked by default.
- Can develop persistent (keeping the data) and non-persistent (momentary) storage.
- Tails verifies and confirms the Tails version you acquire.
- Wipes out the memory (RAM) after every reboot or closure, squashing the opportunity of accessing the delicate information, i.e., passwords, logins, and so on, after restarts/ closures.
- MAC Address Spoofing
Built-in Protection and Personal Privacy Devices for Maximum Anonymity
-
- Tor Network: A Confidential network to course website traffic anonymously.
- Thunderbird: An email client to send/receive encrypted emails.
- KeePassXc: A password manager to safely conserve passwords.
- Electrum: Bitcoin wallet
- OnionShare: Sharing files/media anonymously
- MAT 2: A tool to eliminate metadata from files, i.e., PDF.
- GnuPG (GPG): Tool for securing, signing, and validating e-mails, making use of Public-Key cryptography.
Persistent Vs Non-Persistent Storage in Tails
Before continuing to its arrangement, let’s have a look at the distinction in between Consistent and Non-Persistent.
| Function | Persistent | Non-Persistent |
|---|---|---|
| Information Conserving | Yes | No |
| Boot Time | Mild Longer | Faster than Non-persistent |
| Suggested For | When you want to have the information in the upcoming sessions. | Maximum Privacy |
Just how to Set up and Set up Tails on a USB Drive (Step-by-Step Guide)
Why are you setting up Tails? If the purpose is privacy, you need to produce a non-persistent Live USB However, if the purpose is to learn and carry out, after that you can develop a persistent one to keep the background and some data from the previous sessions.
- Recommended : Use Tails as a Live OS, i.e., a non-persistent OS.
- Not Recommended : Stay clear of installing it on your key host or primary virtual device, where traces can continue.
Equipment Needs for Installing Tails
- 64 -bit cpu
- Minimum 2 GB RAM (Recommended is 4 GB)
- Minimum 8 GB USB drive (Advised is 16 GB)
Step 1: Download and Validate the Tails OS Disk Photo (For USB or Digital Machines)
Download And Install the Tails (either for USB sticks or the ISO file for Virtual makers).

Download Tails:

Once downloaded, confirm your downloaded and install version:

Validate that the confirmation is successful before proceeding additionally:


Step 2: Install Tails
When done, you need to have a USB bootable device like balenaEtcher (if utilizing Linux), Rufus (if utilizing Windows), and so on. Here, I have actually provided two possibilities:
- Setup Alternative 1: Setting Up Tails Utilizing the GNOME Disks Application
- Installment Alternative 2: Installing Tails Making Use Of the Balena Etcher
- Installment Alternative 1: GNOME Disks Application
If you are making use of a GNOME desktop computer atmosphere, you can make the Tails USB making use of the GNOME Disks Desktop application. Right here’s the process.
Attach the USB with the Linux OS, and open the” GNOME Disks app. Now, choose the USB and click the” vertical ellipsis
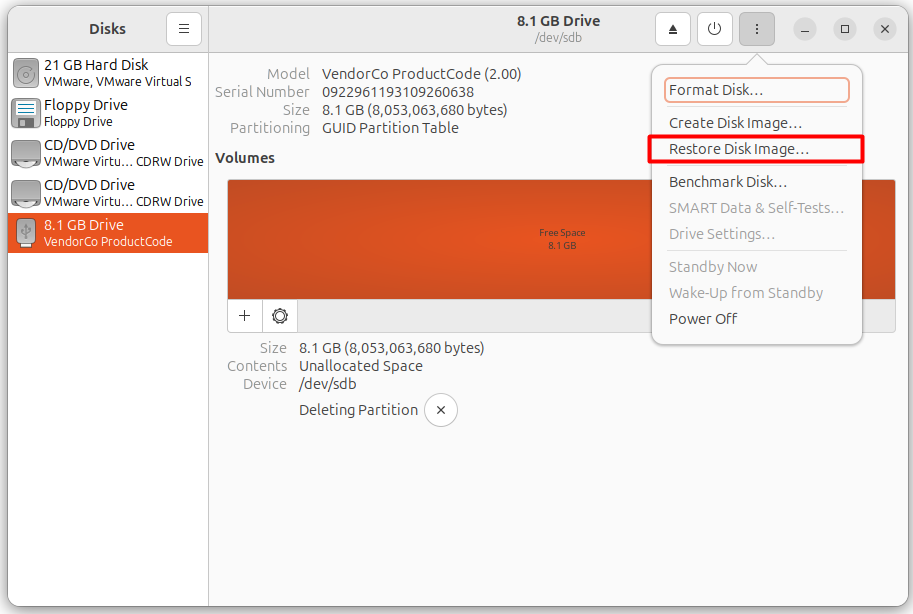

It will certainly after that ask you to choose the Disk Image:
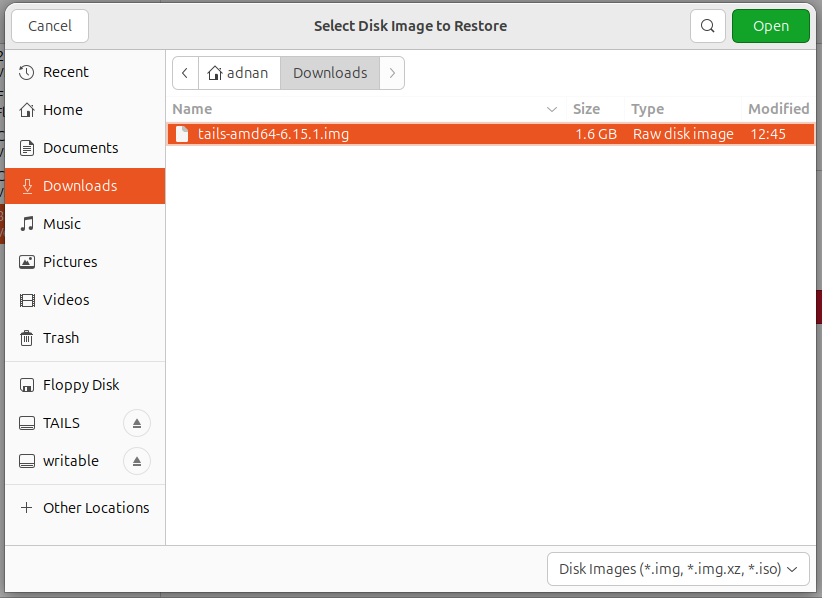

Confirm to start creating Tails on USB:
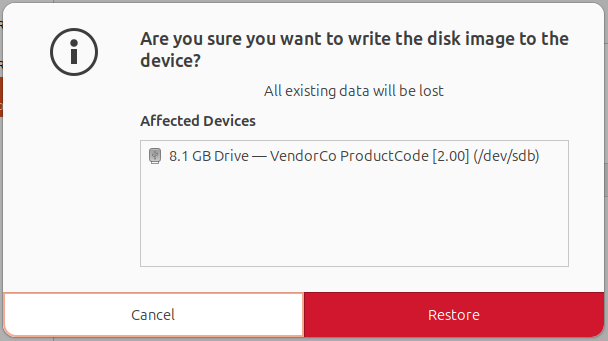

This will certainly take a couple of mins. As soon as all done, you can eject the drive and boot from the USB to run Tails in a separated environment.
- Setup Option 2: Setting Up Tails Utilizing the balenaEtcher
Initially, you have to download and set up the Balena Etcher on your corresponding Linux circulation.
Once mounted, you need to make the USB bootable with the Tails disk picture that you have actually currently downloaded.
Follow this guide to briefly recognize exactly how to set up and utilize Balena Etcher
Setting Up Consistent Storage and Administrator Password
When you boot from Tails, you will certainly have to go through the complying with user interface, where you can develop persistent storage and set the manager password.
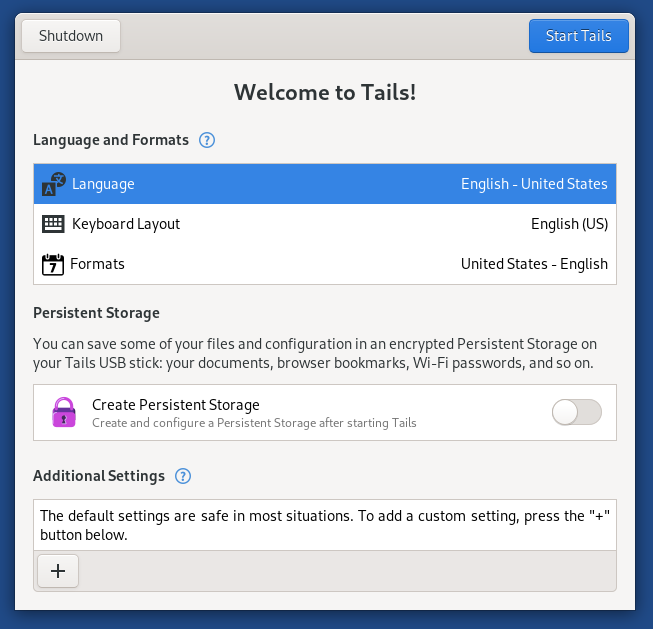

- Relentless Storage: To keep the data, history for additional sessions.
- Manager Password: To manage the authorizations or admin password required for installing applications.
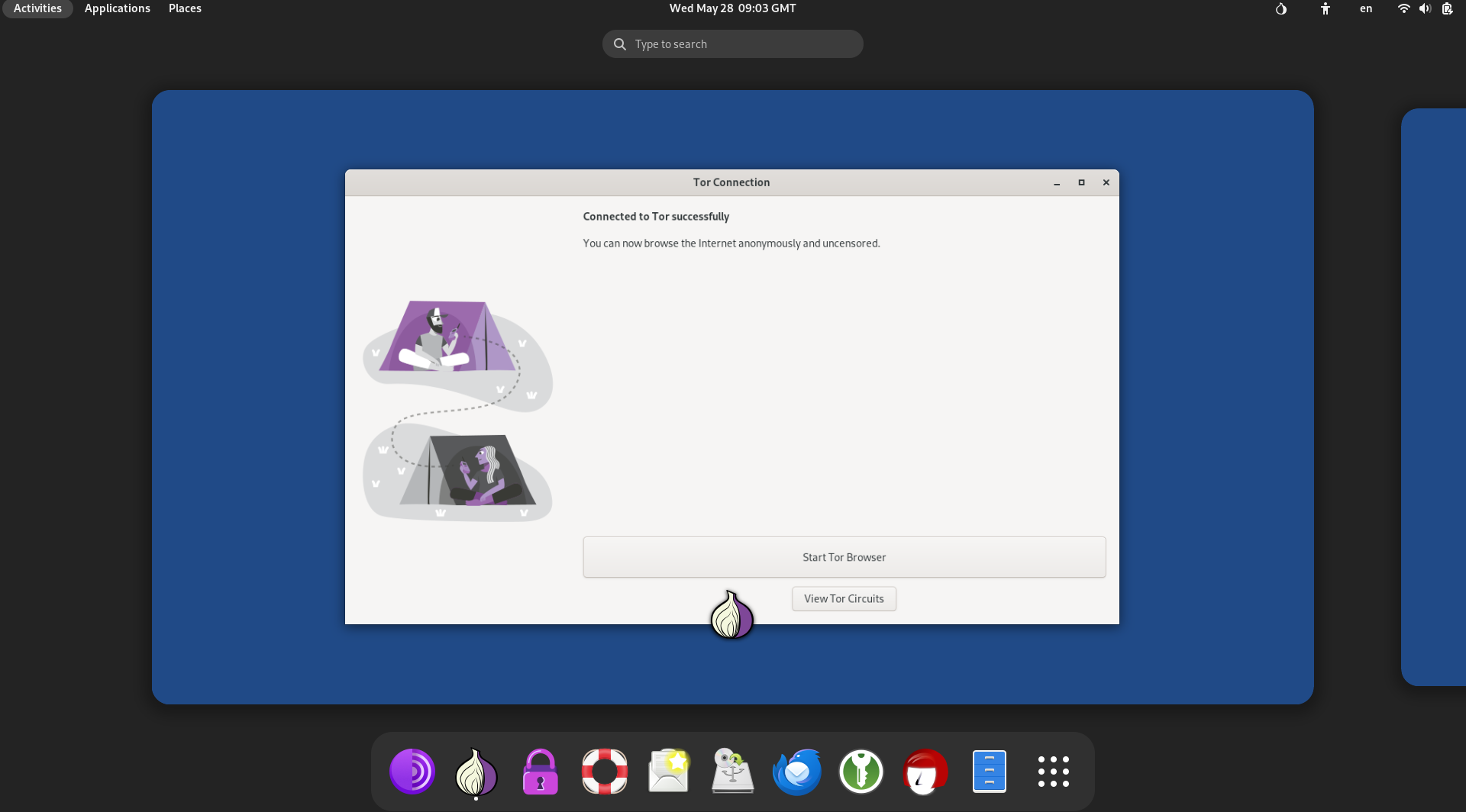
Now, you need to set the Tor connection, where you have 2 options, i.e., select” Connect to Tor automatically
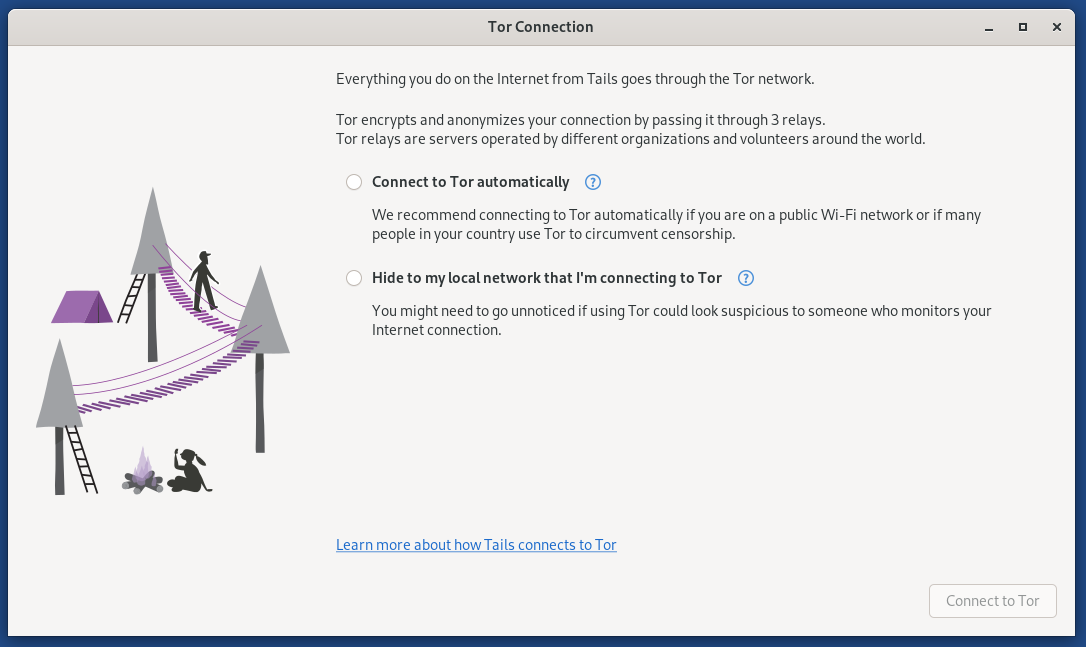

In this manner, you can establish privacy through Tails.
- What is Tor/Onion Circuits : The Path that the Tor network makes use of to path web traffic from a user’s tool to the destination web server with privacy.

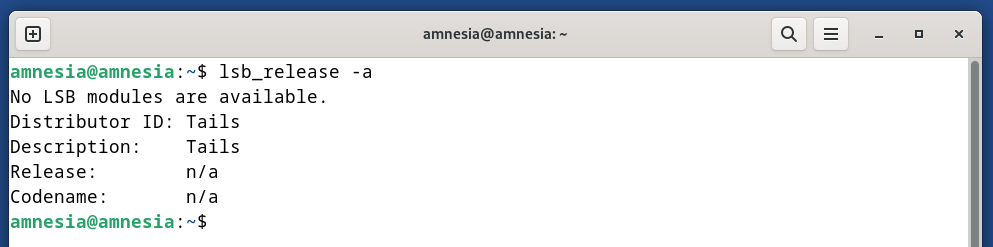
Right here’s the incurable appearance of the Tails:

Here you select the Tails:

Should You Make use of Tails?|Technical Advantages And Disadvantages
If you still have concerns concerning whether Tails is a best fit for me or otherwise, do not stress, I have actually put together a technical Pros/Cons of Tails to help you hereof:
| Technical Feature/Component | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Tor-based Privacy | Courses traffic via the Tor network by default. | Some websites discourage the Tor Project. |
| Data Safety | It’s RAM-dependent, and thus, information is wiped out after every boot, i.e., no data violation or tracing through data | Data is shed, i.e., the new Tails individual who is not familiar with non-persistent working. When the customer is familiar with the system, this problem will certainly reduce. |
| Personal privacy Tools | Integrated tools for file sharing, password, e-mail customer, etc. | Restricted application schedule (outside the default installation) |
| No Installment | Simply plug and play. Plug in the real-time USB of Tails, and you are great to go. No difficult and taxing installments. | Unpredictable performance contrasted to the full-fledged installed system. |
| Equipment Protection | Tails spoofs MAC addresses. So, absolutely nothing past that when it comes to protection. | It might malfunction sometimes, i.e., in a dispute with the net hardware gadgets. |
| Disk Image Confirmation | Disk Image is briefly validated on the Tails main internet site. | It may be challenging for the new or non-technical customers. |
| System Footprint | An extremely little footprint, i.e., negligible, due to the advanced encryption/protection level. | This makes it not ideal for regular or day-to-day tasks. |
| Updates | Constant Updates, i.e., every 6 weeks. | Create a bootable system with every upgrade. |
Pro-Tip: For optimal safety, always utilize the non-persistent USB for Tails and appreciate this state-of-the-art tool in the technology age.
Verdict
Tails OS is just one of the most effective anonymity tools based upon the Debian distro and is a part of the Tor task. With one end in Open Source (Linux-based) and the various other in privacy (Tor task).
Tails OS is installed and utilized as an Online non-persistent USB, which lessens the threat of any traces. Today, I have actually prepared a comprehensive testimonial of the Tails OS, including its setup on a USB also.
FAQs:
Q 1: Is Tails OS Legal?
Yes, Tails is lawful. Tails is an open-source Debian-inspired Tor job. The Onion Routing (Tor) nature of Tails makes it suspicious however not illegal.
Q 2: Does Tails hide your IP?
Tails is a Tor project, and when transmitting, it hides your IP and web server information.
Q 3: Does Tails run in RAM?
Because it’s an amnestic, no information or history is kept. This anonymity is because of RAM. It briefly shops data and rejuvenates it after each session.
Q 4: What is the Tails filesystem?
Tails deal with the Ext 4 file system, i.e., 4th Extended Filesystem.
